 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator computes the volume and surface area of a parallelepiped using three different methods: vectors, sides and angles, or sides and height.
Purpose: Useful for geometric calculations in mathematics, physics, and engineering.
The calculator offers three methods to compute the volume:
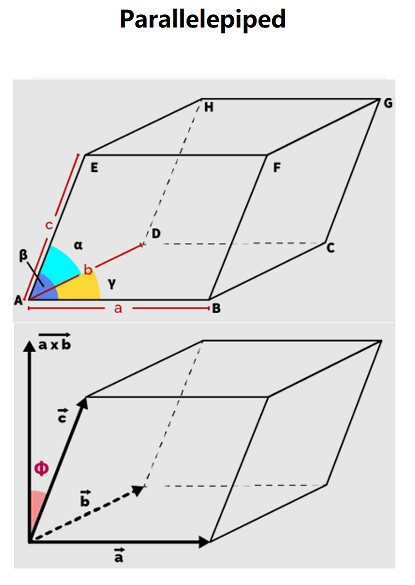
Method 1: Using Three Vectors
Compute the cross product \( \vec{a} \times \vec{b} \), then the dot product with \( \vec{c} \), and take the absolute value.
Method 2: Using Sides and Angles
Where \( a, b, c \) are adjacent sides, \( \alpha \) is the angle between \( b \) and \( c \), \( \beta \) is between \( a \) and \( c \), and \( \gamma \) is between \( a \) and \( b \).
Method 3: Using Sides and Height
Where \( a \) and \( b \) form the base, and \( h \) is the height perpendicular to the base.
Surface Area (All Methods)
Unit Conversions:
Details: Calculating the volume and surface area of a parallelepiped is essential in geometry, physics, and engineering applications.
Tips: Select a method, then enter the required inputs (vectors, sides and angles, or sides and height) in mm, cm, m, in, or ft (all >0, angles 0-180°). Results show the volume (cm³, in³, ft³, m³) and surface area (cm², in², ft², m²).