 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator computes the surface area, volume, and surface area to volume ratio for various basic shapes.
Purpose: Useful for understanding geometric properties in mathematics, biology, and engineering.
| Shape | Surface Area | Volume | Surface Area to Volume Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
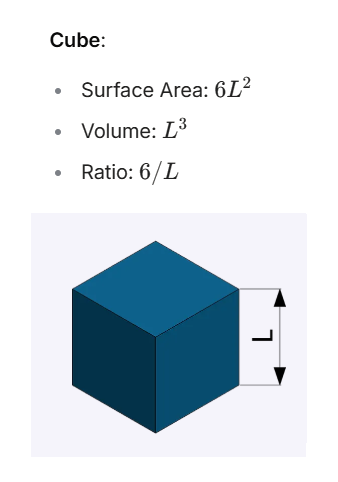
| Cube | \( 6L^2 \) | \( L^3 \) | \( 6/L \) |
| Cylinder | \( 2\pi R (R + H) \) | \( \pi R^2 H \) | \( 2 (R + H) / (R H) \) |
| Sphere | \( 4\pi R^2 \) | \( 4\pi R^3 / 3 \) | \( 3 / R \) |
| Cone | \( \pi R L + \pi R^2 \) (where \( L = \sqrt{R^2 + H^2} \)) | \( \pi R^2 H / 3 \) | \( 3 (R + L) / (R H) \) |
| Hemisphere | \( 3\pi R^2 \) | \( 2\pi R^3 / 3 \) | \( 4.5 / R \) |
| Capsule | \( 2\pi R (2R + H) \) | \( \pi R^2 (4R/3 + H) \) | \( (2R + H) / (4R + 3H) \) |
Unit Conversions:
Details: The surface area to volume ratio is crucial in biology (e.g., cell efficiency), engineering (e.g., heat dissipation), and material science.
Tips: Select a shape and enter the required dimensions (length, radius, height) in mm, cm, m, in, or ft (all >0). Results show surface area (cm², in², ft², m²), volume (cm³, in³, ft³, m³), and the ratio.